The realm of sports psychology has long been fascinated by the subtle yet powerful influence of mental cues on athletic performance. Among these, the concept of sporting psychological—often referred to as "sporting mental" or "athletic"—has emerged as a critical tool for athletes seeking to unlock their full potential. Unlike overt motivational speeches or structured training regimens, these operate on a subconscious level, quietly shaping an athlete’s mindset, focus, and even physical responses during competition. The science behind this phenomenon reveals how deeply intertwined the mind and body truly are in the context of sports.
At its core, sporting psychological leverages the brain’s ability to internalize cues and translate them into actionable outcomes. For instance, a sprinter might repeat a specific phrase or visualize a particular scene before a race, effectively programming their mind to trigger peak performance when it matters most. This process isn’t merely about positive thinking; it’s about creating neural pathways that align with desired physical actions. Studies have shown that athletes who consistently use such exhibit improved reaction times, greater endurance, and enhanced emotional resilience under pressure. The implications are profound, suggesting that mastery of one’s mental landscape can be as vital as physical training.
One of the most intriguing aspects of sporting is its versatility across disciplines. From marathon runners to chess players, the application of tailored mental cues has demonstrated measurable benefits. A tennis player might focus on the rhythmic sound of their breath to maintain calm during a high-stakes match, while a weightlifter could use a single word to summon explosive power at the critical moment. What unites these examples is the deliberate use of sensory or cognitive triggers to bypass conscious doubt and access a state of flow. This universality underscores’s role as a democratizing force in sports psychology—accessible to amateurs and professionals alike.
The physiological mechanisms behind these effects are equally compelling. When an athlete employs a well-practiced, the brain often responds by releasing neurotransmitters like dopamine and endorphins, which enhance focus and reduce perceived pain. Simultaneously, cortisol levels—the hormone associated with stress—may decrease, creating an optimal internal environment for performance. This biochemical shift explains why seasoned athletes frequently describe feeling "in the zone" when their rituals are executed flawlessly. It’s not magic; it’s the result of meticulously trained mental processes producing tangible physical outcomes.
However, the effectiveness of sporting isn’t guaranteed without proper implementation. Research indicates that the most successful cues are those deeply personalized to the athlete’s experiences and goals. A generic mantra like "I can do this" might yield modest results, but a rooted in an athlete’s past triumphs or tailored to their specific anxieties can be transformative. This personalization often requires collaboration with sports psychologists to identify triggers that resonate on an individual level. The process mirrors the customization of physical training plans, emphasizing that mental preparation is equally nuanced and deserving of attention.
Critically, the timing and context of deployment also influence their efficacy. Pre-competition often differ from those used mid-performance or during recovery periods. A basketball player might use a visualization technique before a game to instill confidence but switch to a breath-focused during free throws to combat pressure in real-time. This dynamic application highlights how must evolve with an athlete’s shifting needs throughout their competitive journey. It’s a skill that, like any other, improves with practice and refinement over time.
The cultural dimension of sporting adds another layer of complexity. Different athletic traditions have developed unique approaches to mental preparation—from the mindfulness practices in Eastern martial arts to the ritualistic behaviors common in Western team sports. These variations remind us that while the science of暗示 may be universal, its expression is deeply cultural. Modern athletes increasingly borrow across these traditions, creating hybrid strategies that reflect our globalized sports landscape. This cross-pollination enriches the toolkit available to competitors seeking every possible edge.
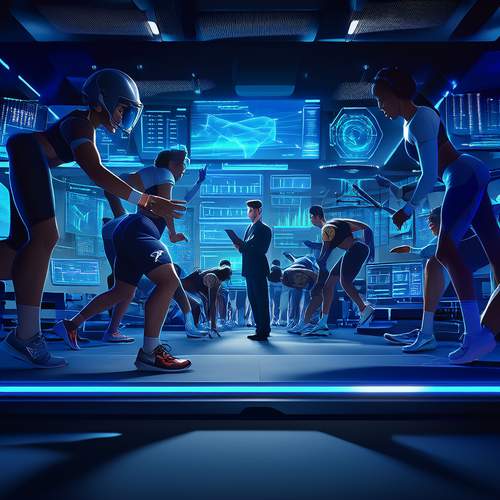
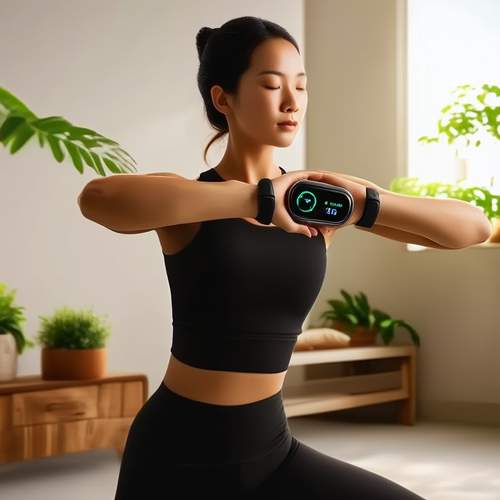
Technology’s role in enhancing sporting has grown exponentially in recent years. Biofeedback devices now allow athletes to observe their physiological responses to different in real-time, creating a data-driven approach to mental training. Virtual reality simulations enable competitors to practice their techniques in hyper-realistic competitive scenarios, strengthening the mind-body connection. These advancements are pushing beyond its traditional boundaries, offering unprecedented precision in mental preparation. Yet, the human element remains irreplaceable—the athlete’s willingness to engage deeply with their own psyche still determines success.
Looking ahead, the study of sporting psychological promises to revolutionize how we understand peak athletic performance. As neuroscience uncovers more about the brain’s plasticity and its relationship to physical action, the line between mental and physical training will continue to blur. Future athletes may spend as much time honing their techniques as they do their physical skills, recognizing that victory often begins in the mind. For now, the growing adoption of these practices across sports at all levels signals a paradigm shift—one that acknowledges the silent power of the thoughts we cultivate before, during, and after competition.

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025
By /May 21, 2025
By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025

By /May 21, 2025